Table Unions
Table unions are used when it is necessary to merge 2 or more type compatible answer tables into ONE distinct list.
Type compatibility refers to the datatype and order of the columns selected in the tables to be merged. The resultant answer table, as a side effect, produces a distinct (unique) list of tuples.
Q:
List alphabetically all artists or groups featured in the music database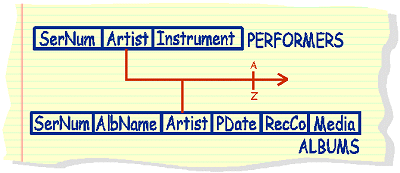 |
select
Artist from Performers union select Artist from Albums order by 1 |
Q:
List a 3 column table, one column to contain either "new"
or "old" depending on whether the album was published before
1980, that also contains album names and the group name who released
it. Present the answer table arranged alphabetically on artist.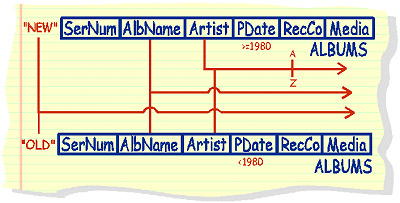 |
select
"new", AlbName, Artist from Albums where PDate >= 1980 union select "old", AlbName, Artist from Albums where PDate <1980 order by 3 |
Unions are immensly useful when you need to output a collection of human friendly labels amongst existing data, as with the 2nd example above.
Ordering of a union query involves the compulsory use of column numbers rather that column names (as the resultant answer table loses track of which column is names which, even though it will present column names with the answer table).
The symbols used above borrow heavily from circuitry diagrams. As it is often unavoidable to cross over other dataflows, the speed bump intersection attempts to counteract this.
Data flows from columns that are to be unioned converge into a single data flow arrow - meaning 2 columns coalesce or merge into one.